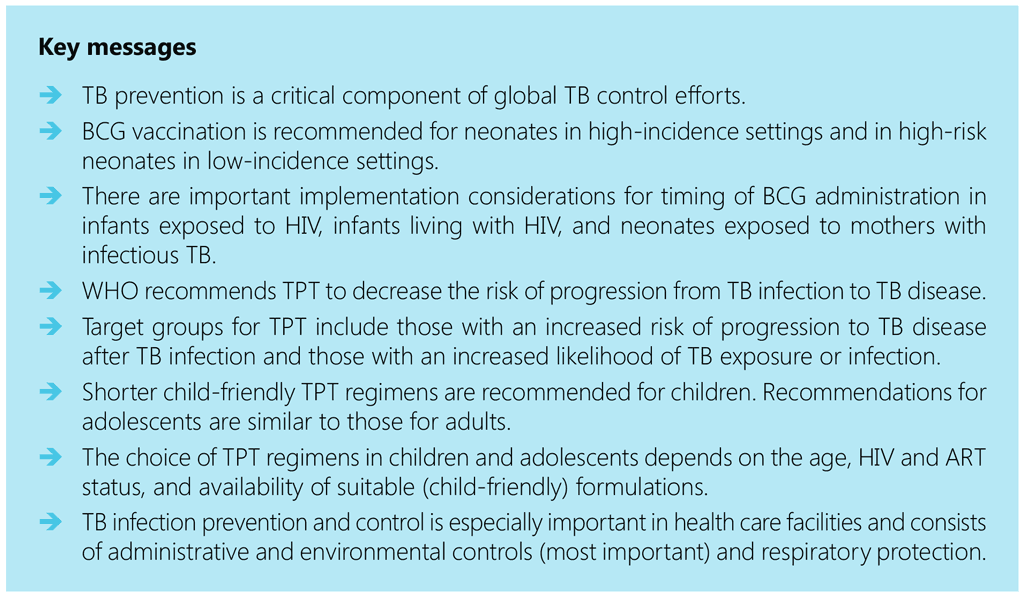
Children and Adolescents
3.2.1.4. Adverse reactions
BCG vaccine is used extensively worldwide, with about 100 million newborns vaccinated each year. Severe adverse events are reported only occasionally. For some adverse events (e.g. disseminated BCG disease), the diagnosis may depend on the culturing of M. bovis BCG to distinguish it from other forms of mycobacterial disease (33). It is important to recognize that M.
Annex 7. Overview of options for neurocognitive and functional testing at end of treatment for TB meningitis
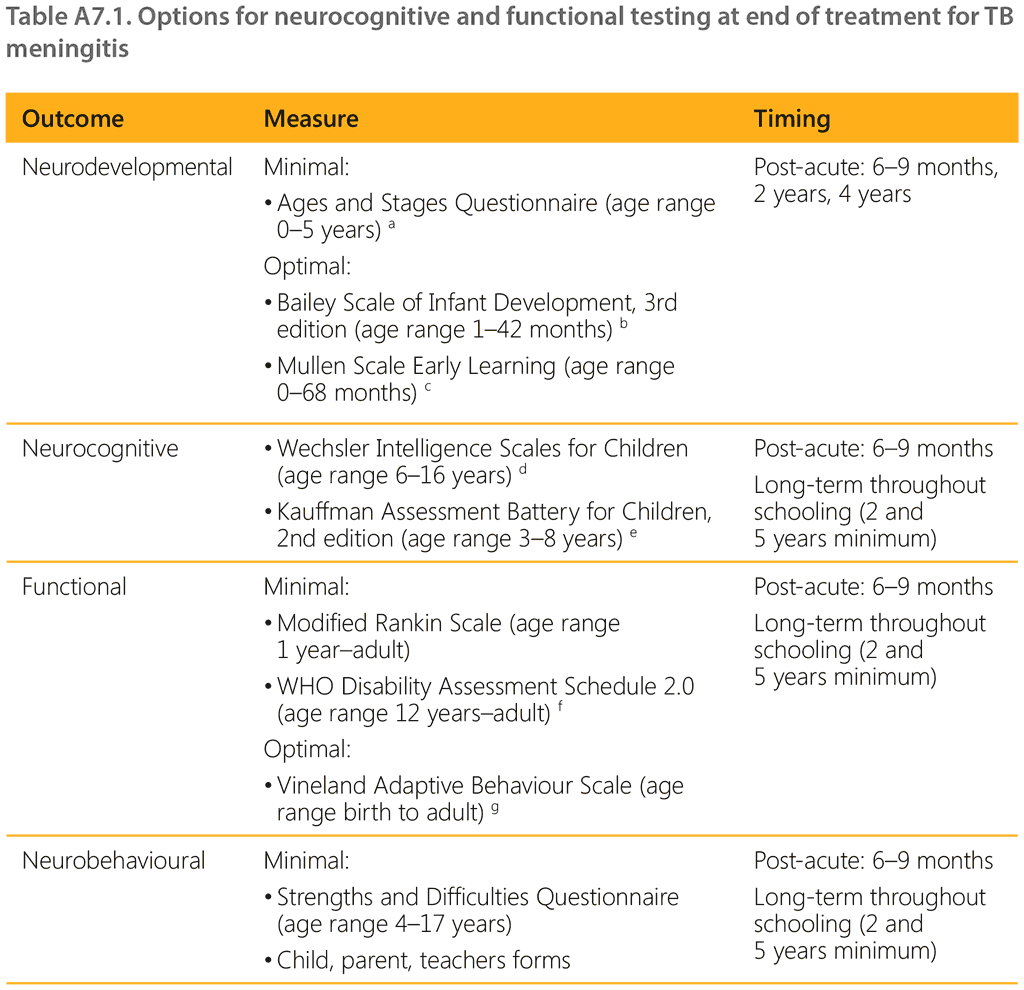
Note: these developmental assessment tools have not been formally adapted for use in low- and middle-income countries, and locally determined norms have not been developed. Interpretation of results requires careful consideration of the local context. A number of in-country locally developed screening tools are also available.
Annex 6. Dosing of medicines used in second-line multidrug-resistant TB regimens by weight band (below 46 kg)
- Dosing guidance is based on currently available data and may be revised once additional data are available.
- For patients weighing ≥46 kg, please refer to Table A in Annex 1 of the WHO operational handbook on tuberculosis.
Annex 5. Treatment decision algorithms
Methodology for developing the treatment decision algorithms
Annex 4. Standard operating procedures for sample collection methods
This annex provides examples of standard operating procedures for the most common methods of obtaining clinical samples from children for rapid molecular testing: expectoration, gastric aspiration, nasopharyngeal aspiration (NPA) and sputum induction.
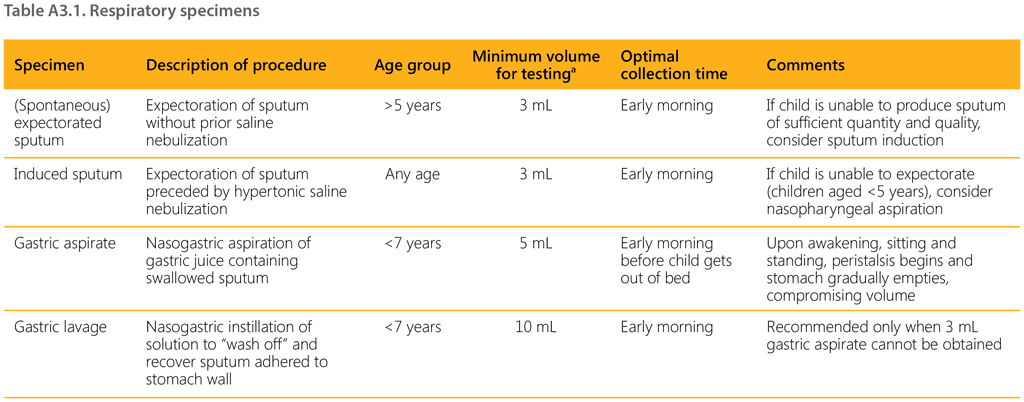
Annex 3. Sample collection methods
This annex provides an overview of respiratory and non-respiratory specimens that can be used to diagnose TB in children and adolescents, with a short description for each, the age group in which they can be used, the minimum volume required for testing, and the optimal time of collection.
Annex 2. Tuberculin skin testing: administration, reading and interpretation
This annex provides information on administering, reading and interpreting tuberculin skin tests (TSTs).
A TST is the intradermal injection of a combination of mycobacterial antigens that elicit a delayed-type hypersensitivity immune response, represented by induration, which can be measured in millimetres.
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page
 Feedback
Feedback