Links de passagem do livro para 5.2.1 Ethionamide variation
The ethionamide variation involves the initiation of bedaquiline, levofloxacin/moxifloxacin, clofazimine, ethionamide, ethambutol, isoniazid (high dose) and pyrazinamide. All seven drugs are given for 4 months, with the possibility of extending to 6 months if the patient’s sputum remains bacteriologically positive at the end of the fourth month on treatment. Ethionamide and high-dose isoniazid are dropped after 4 or 6 months, depending on the decision to extend treatment based on smear status at month 4 of treatment. This is followed by 5 months of treatment with levofloxacin/moxifloxacin, clofazimine, ethambutol and pyrazinamide. Bedaquiline is usually given for 6 months but could be extended to 9 months, particularly if the initial phase is extended from 4 to 6 months due to a lack of sputum conversion at month 4.
The regimen is summarized as:
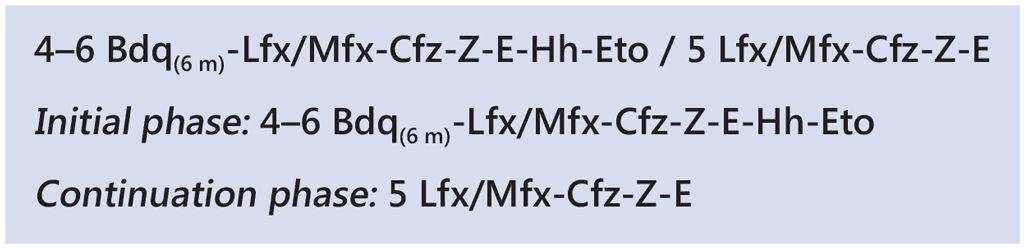
 Opinião
Opinião