Book traversal links for 7. Special situations
This chapter includes valid WHO recommendations that apply to children and adolescents in special situations such as for the management of TB in the context of HIV infection or malnutrition and optimal feeding of infants of mothers infected with TB. The recommendations have been consolidated from several current WHO guidelines on TB/HIV coinfection and nutrition, namely the WHO policy on collaborative TB/HIV activities: guidelines for national programmes and other stakeholders (124), the Consolidated guidelines on HIV prevention, testing, treatment, service delivery and monitoring: recommendations for a public health approach, July2021 (125), the Guideline: updates on the management of severe acute malnutrition in infants and children, 2013 (60), and the Guideline: Nutritional care and support for patients with tuberculosis, 2013 (126). For more information on each recommendation including the remarks, source of evidence, justification, subgroup-, implementation- and monitoring and evaluation considerations, the source guidelines or WHO TB KSP should be consulted.

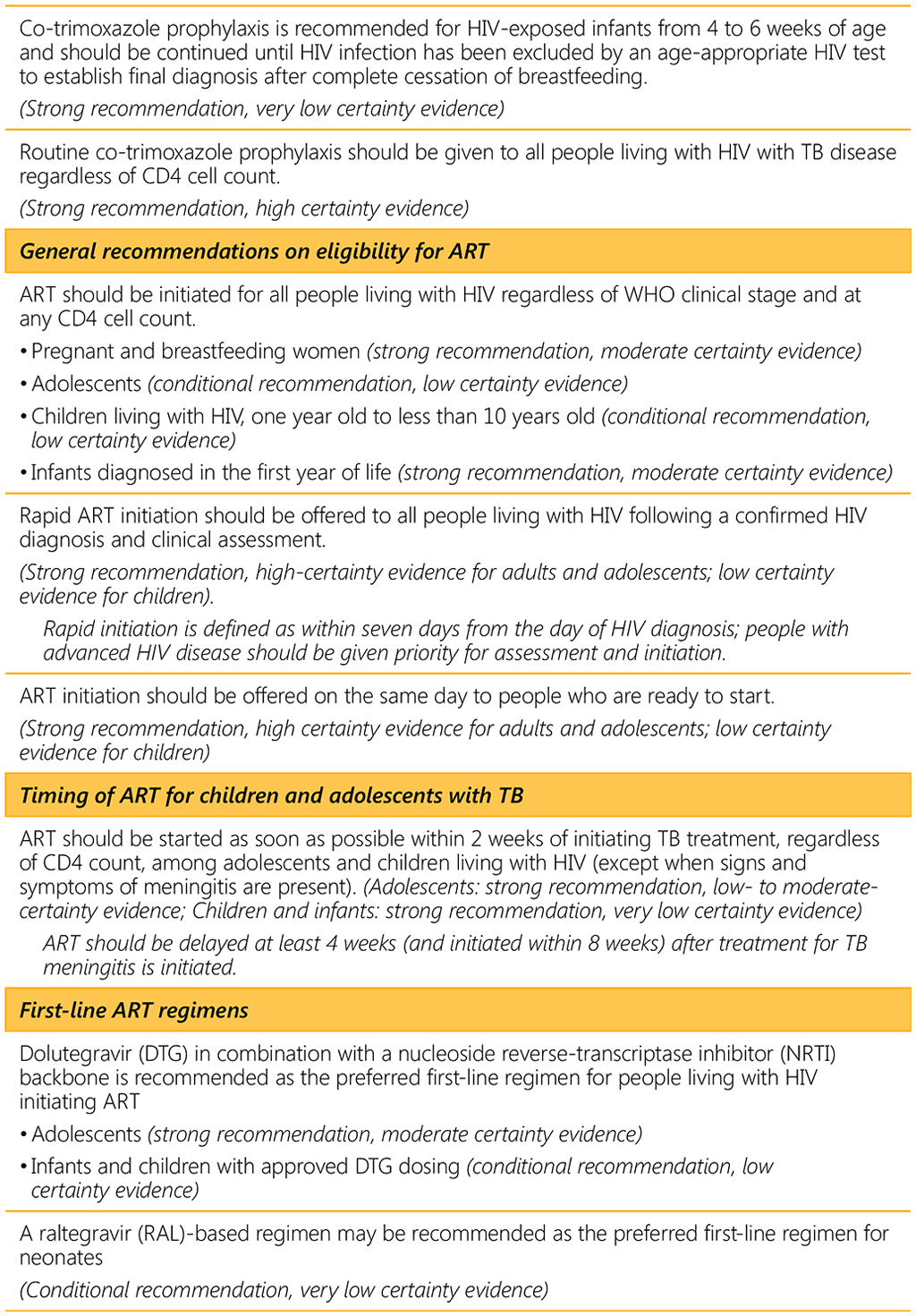
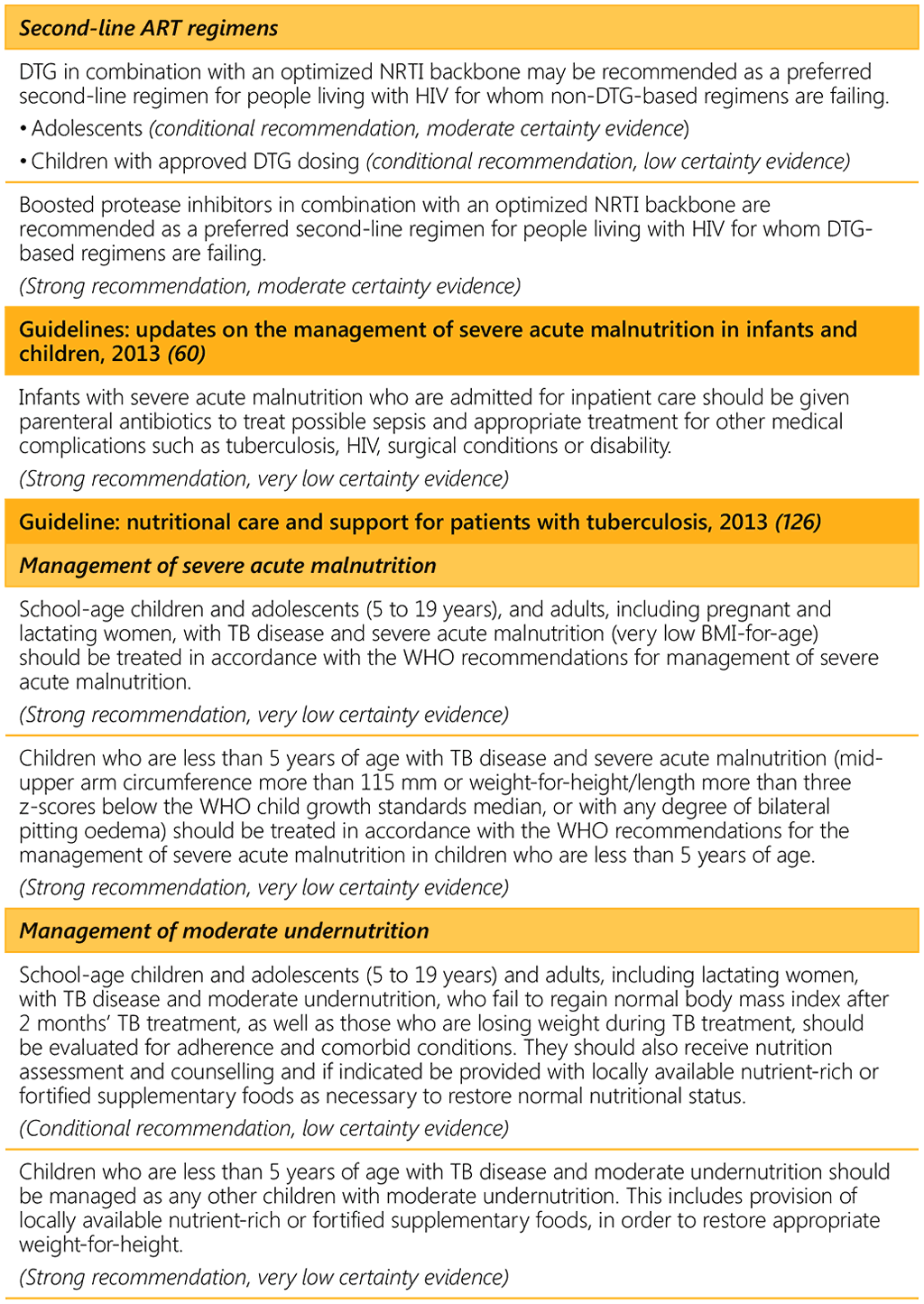

⁴⁵ Pyridoxine supplementation is recommended along with isoniazid treatment for all pregnant (or breastfeeding) women, as well as for people with conditions such as HIV infection, alcohol dependency, malnutrition, diabetes, chronic liver disease or renal failure. Pyridoxine provision together with isoniazid treatment was not analysed for the 2013 nutrition guideline.
 Feedback
Feedback