Book traversal links for 1.3 Determining risks
Risk is the combination of the likelihood that a specific hazard will be encountered and the consequences of an event related to that specific hazard. Risks should be identified and categorized, and a determination should be made about which risks need to be controlled or minimized. The analysis of aerosolization risks described in this manual has led to the development of minimum biosafety requirements necessary for performing different procedures in TB laboratories.



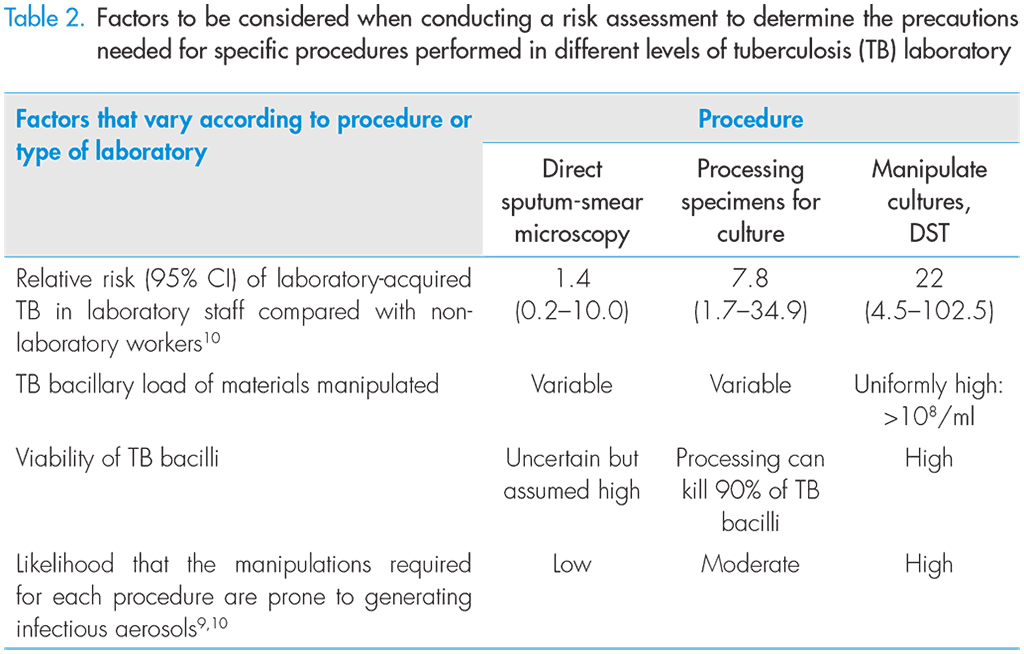
Based on their assessment of the procedural risks usually encountered in TB laboratories in resource-limited high-burden settings, the Expert Group developed minimum requirements needed to ensure safety for staff conducting different procedures used to diagnose TB. Whenever possible, every laboratory should conduct their own risk assessment to determine which additional measures need to be put in place to provide suitable protection to their laboratory technicians.
The recommendations described in this document are meant to inform national policies and do not supersede or replace any national rules or regulations. The minimum requirements needed to reduce risks in TB laboratories are described in chapters 3, 4 and 5.
MDR, multidrug-resistant; XDR, extensively drug-resistant.
ᵃ Number extrapolated from animal studies.
CI, confidence interval; DST, drug-susceptibility testing.
 Feedback
Feedback