Book traversal links for Truenat MTB, MTB Plus and MTB-RIF Dx assays
New molecular assays – the Truenat MTB, MTB Plus and MTB-RIF Dx assays (Molbio Diagnostics, Goa, India), hereafter referred to as Truenat – were developed in India, and may be used at the same health system level as Xpert MTB/RIF. Of the above-mentioned assays, MTB and MTB Plus are used as initial diagnostic tests for TB, whereas MTB-RIF Dx is used as a reflex test to detect rifampicin resistance for those with positive results on the initial Truenat tests. Multisite international evaluations in settings of intended use are being implemented by the Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND), a WHO collaborating centre for the evaluation of new diagnostic technologies. Given the similarity of the operational characteristics for Xpert MTB/RIF and Truenat, the results of the latter study were reviewed within the same GDG meeting.
Recommendations
Recommendations on Truenat MTB, MTB Plus and Truenat MTB-RIF Dx in adults and children with signs and symptoms of pulmonary TB
- In adults and children with signs and symptoms of pulmonary TB, the Truenat MTB or MTB Plus may be used as an initial diagnostic test for TB rather than smear microscopy/culture.
(Conditional recommendation, moderate certainty of evidence for test accuracy) - In adults and children with signs and symptoms of pulmonary TB and a Truenat MTB or MTB Plus positive result, Truenat MTB-RIF Dx may be used as an initial test for rifampicin resistance rather than culture and phenotypic DST.
(Conditional recommendation, very low certainty of evidence for test accuracy)
Remarks
For recommendation 1: The recommendation includes patients who are smear negative. There is uncertainty about the use of these assays in PLHIV. In smear-negative patients, the sensitivity is lower than in all patients. The indirect data on test accuracy in smear-negative patients (given that there are no data on PLHIV for this version of Truenat) made it possible to extrapolate this recommendation to PLHIV. However, the certainty of evidence for test accuracy would need to be lowered to account for additional indirectness. In the case of children, there were no data available to assess the accuracy of the test in different specimens, and not enough indirect evidence to extrapolate for specimens other than sputum. This recommendation is extrapolated to children for sputum, although the tests are expected to be less sensitive in children.
For recommendation 2: The Truenat aplies a reflex (two-step) test for rifampicin resistance. Hence, the recommendation for Truenat MTB-RIF Dx is only applicable for those patients with positive Truenat MTB or MTB Plus results.
Test descriptions
The new molecular assays – the Truenat MTB, MTB Plus and MTB-RIF Dx assays – developed in India, may be used at the same health system level as Xpert MTB/RIF. This policy focuses on the following Molbio devices and diagnostic tests (13):
- Trueprep Auto DNA extraction system;
- Truelab DuoDx and Truelab QuattroDx micro-PCR machines;
- Truelab MTB chip;
- Truelab MTB Plus chip; and
- Truelab MTB-RIF Dx chip.
The Truenat MTB and MTB Plus assays and the rifampicin-resistance detection reflex assay (Truenat MTB-RIF Dx) (Molbio Diagnostics, India) use real-time micro-PCR for detection of M. tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in DNA extracted from a patient’s sputum specimen (Fig. 2.1.3). The assays use automated, battery-operated devices to extract, amplify and confirm the presence of specific genomic DNA loci, allowing for the rapid diagnosis of TB infections with minimal user input. These products are intended to be operated in peripheral laboratories with minimal infrastructure, and technicians with only minimal training can easily perform these tests routinely in their facilities and report results in under 1 hour. Moreover, with these devices, PCR testing can also be initiated at the field level, on-site.
If the Truenat MTB assay result is positive, the user may then take another aliquot of extracted DNA and run the MTB-RIF Dx assay, to detect the presence of selected rifampicin-resistanceassociated mutations. The diagnostic performance of these assays has been previously evaluated in microscopy centres in India, (13) but a larger assessment of the operational characteristics and acceptability of the technology is needed in intended settings of use to confirm assay performance.
Fig. 2.1.3. Molbio equipment to run the Truenat MTB, MTB Plus and MTB-RIF Dx assays: (a) Trueprep instrument for sample preparation, (b) Truelab Uno Dx real-time PCR instrument for running the tests, and (c) chip for real-time PCR

Justification and evidence
The evidence on the use of the Truenat MTB, MTB Plus and MTB-RIF Dx system was generated by multisite international evaluations in settings of intended use, implemented by FIND.
The PICO questions were designed to form the basis for the evidence search, retrieval and analysis.
The evaluation study of Truenat was carried out in 19 clinical sites (each with a microscopy centre attached) and seven reference laboratories in four countries. The diagnostic accuracy of the assays was evaluated when performed in the intended settings of use (i.e. microscopy centres), against microbiological confirmation (culture) as the reference standard. As part of this assessment, the performance of the Truenat assays was also compared to Xpert MTB/RIF or Xpert Ultra, on the same specimens, in reference laboratories. The certainty of the evidence was assessed consistently through PICO questions, using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach, which produces an overall quality assessment (or certainty) of evidence and a framework for translating evidence into recommendations. The certainty of the evidence is rated as high, moderate, low or very low. These four categories “imply a gradient of confidence in the estimates” (10). In the GRADE approach, even if diagnostic accuracy studies are of observational design, they start as high-quality evidence.
At least two review authors independently completed the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies (QUADAS)-2 assessments. Any disagreements were resolved through discussion or consultation with a third review author.
Data synthesis was structured around the preset PICO questions list below. Details of study included in the current analysis are given in Web Annex 1.2: Truenat MTB, MTB Plus and MTB-RIF Dx. Summary of the results and details of the evidence quality assessment are available in Web Annex 2.2: Truenat MTB, MTB Plus and MTB-RIF Dx.
PICO 7: Among people with signs and symptoms of pulmonary TB, seeking care at health care facilities, should Molbio Truenat MTB, MTB Plus and MTB-RIF Dx be used as an initial test for diagnosis of pulmonary TB and rifampicin resistance?
6.4 What is the diagnostic accuracy of Truenat MTB to diagnose pulmonary TB in adults with signs and symptoms of pulmonary TB, as compared with MRS?
Evidence for the use of Truenat MTB, MTB Plus and MTB-RIF Dx assays to diagnose pulmonary TB and rifampicin resistance in adults was generated through a multicentre prospective clinical evaluation study implemented by FIND. The study was conducted at 19 clinical sites (each with a microscopy centre attached) and seven reference laboratories in four countries. The aim was to determine the diagnostic accuracy of the Truenat assays when performed in the intended settings of use (i.e. microscopy centres), relative to microbiological confirmation (culture) as the reference standard. The performance of the Truenat assays was also compared head-to-head (on the same specimens) to Xpert or Ultra in reference laboratories, as part of this assessment. All sites performed Xpert except for sites in Peru, which performed Ultra. The analysis for Truenat MTB reported on the results for 1336 participants. Serious concerns were expressed for imprecision and inconsistency of evidence related to sensitivity. Overall, the certainty of evidence was judged to be low for sensitivity but high for specificity.
6.5 What is the diagnostic accuracy of Truenat MTB Plus to diagnose pulmonary TB in adults with signs and symptoms of pulmonary TB, as compared with MRS?
The analysis for Truenat MTB Plus reported on the results for 1336 participants. Serious concerns were expressed for imprecision for sensitivity, related to the few participants contributing to the analysis. Overall, the certainty of evidence was judged to be low for sensitivity and high for specificity.
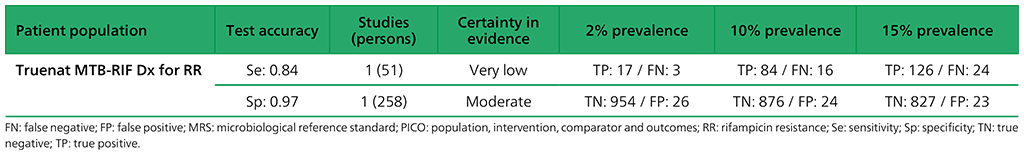
6.6 What is the diagnostic accuracy of Truenat MTB-RIF Dx to diagnose rifampicin resistance in adults with signs and symptoms of pulmonary TB, as compared with MRS?
The analysis for Truenat MTB-RIF Dx reported on the results for 186 participants. For sensitivity, there were serious concerns about indirectness (India and Peru contributed most of the data to the determination of rifampicin resistance) and inconsistency (variable sensitivity estimates: 100% for Peru, based on seven rifampicin-resistant specimens; 100% for Ethiopia, based on one rifampicin-resistant specimen; 100% for Papua New Guinea, based on one rifampicin-resistant specimen; and 81% for India, based on 42 rifampicin-resistant specimens). These results may not be applicable to other settings. In addition, very serious concerns were expressed for imprecision, owing to the small number of participants contributing to this analysis. Overall, the certainty of evidence was judged to be very low for sensitivity. Serious concerns were expressed for indirectness for specificity, related to the low numbers of rifampicin-resistant cases and the fact that most of them were from India and Peru.
Web Annex 4.7: Report on the diagnostic accuracy of the Molbio Truenat tuberculosis and rifampicin-resistance assays in the intended setting of use.
Performance of the molecular assays
Table 2.1.19. PICO 1: What is the diagnostic accuracy of Molbio Truenat MTB for pulmonary TB in adults, as compared with MRS?
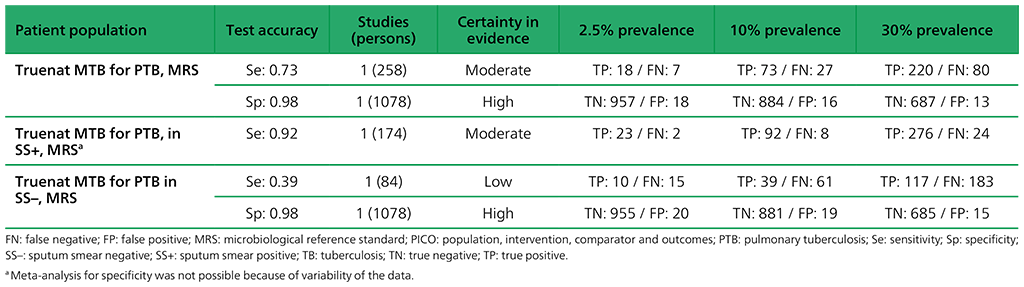
Table 2.1.20. PICO 2: What is the diagnostic accuracy of Molbio Truenat MTB Plus for pulmonary TB in adults, as compared with MRS?
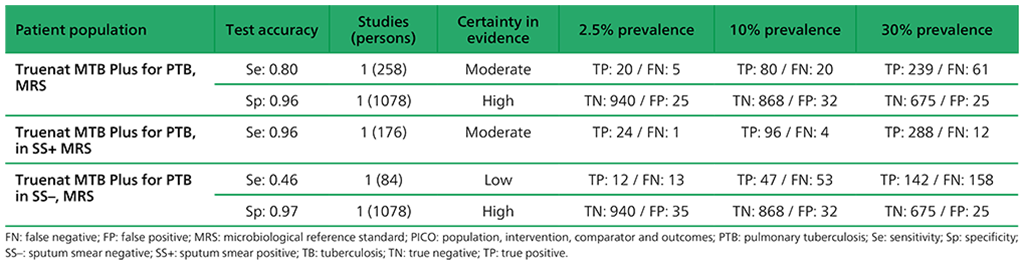
Table 2.1.21. PICO 3: What is the diagnostic accuracy of Molbio Truenat MTB-RIF Dx for rifampicin resistance in adults, as compared with MRS?
Cost–effectiveness analysis
This section deals with the following additional question:
What are the comparative cost, affordability and cost-effectiveness of implementation of Truenat MTB, MTB Plus and MTB-RIF Dx systems?
A systematic review was carried out, focusing on economic evaluations of molecular-based tests for the diagnosis of active TB including the novel Molbio Truenat MTB test. The objective of the review was to summarize current economic evidence and further understand the costs, cost-effectiveness and affordability of these molecular tests for TB diagnosis.
Only one study assessing the cost-effectiveness of Molbio's Truenat MTB was identified. This study suggests that Truenat MTB is likely to be cost effective if implemented at the point of care in India. However, the study relies on several important modelling assumptions, including improved linkage to care and increased treatment initiation; these assumptions should be evaluated in pragmatic trials (as has been done for Xpert MTB/RIF implementation in South Africa).
Caution should be used when generalizing cost-effectiveness and economic evaluations across settings. Local implementation conditions and settings should be taken into account, and local implementation studies may be helpful to assess the likely impact on case finding, long-term outcomes and cost-effectiveness.
More details on economic evaluation of Truenat MTB, MTB Plus and MTB-RIF Dx systems are available in Web Annex 4.5: "Systematic literature review of economic evidence for molecular assays intended as initial tests for the diagnosis of pulmonary and extrapulmonary TB in adults and children".
User perspective
This section deals with the following question:
Are there implications for patient values, feasibility, accessibility and equity from the implementation of Truenat MTB, MTB Plus and MTB-RIF Dx systems?
The available results of the qualitative research were based on Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra mainly for the patient and policymaking perspective (see User perspective for Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra, p. 49 above). Whereas largely qualitative evidence from Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra were judged as applicable to the Truenat tests, caution should be used when generalizing the conclusions, as specific characteristics of the technology, i.e. diagnostic accuracy and use in particular patient populations may be different. Additionally, particularities of supply chain and maintenance relevant for programme staff/managers may also differ. In general, caution should be applied when generalizing findings across settings. The Truenat implementation trial provided information from laboratory technicians perspective on use of the test. Results of the trial showed that test was generally considered as acceptable and feasible by laboratory staff, yet some noted that test is new and more complex to perform compared with Xpert MTB/RIF.
More details on qualitative evaluation of Truenat MTB, MTB Plus and MTB-RIF Dx systems are available Web Annex 4.7: Report on the diagnostic accuracy of the Molbio Truenat tuberculosis and rifampicin-resistance assays in the intended setting of use.
Research priorities
- Operational research to ensure that tests are used optimally in settings of intended use.
- Evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy of Truenat (MTB, MTB Plus and MTB-RIF) in specific patient populations such as PLHIV, former TB patients for pulmonary TB and extrapulmonary TB in adults and children.
 Feedback
Feedback