Book traversal links for 3.3.5.2. Dosages
The WHO task force on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics analysed available evidence from clinical trials of rifapentine and suggested a simplified dose for various weight bands for 3HP and 1HP for the 2020 WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis. Module 1: prevention – tuberculosis preventive treatment (28). Table 3.2 presents standard dosing for the recommended TPT regimens by age and body weight.
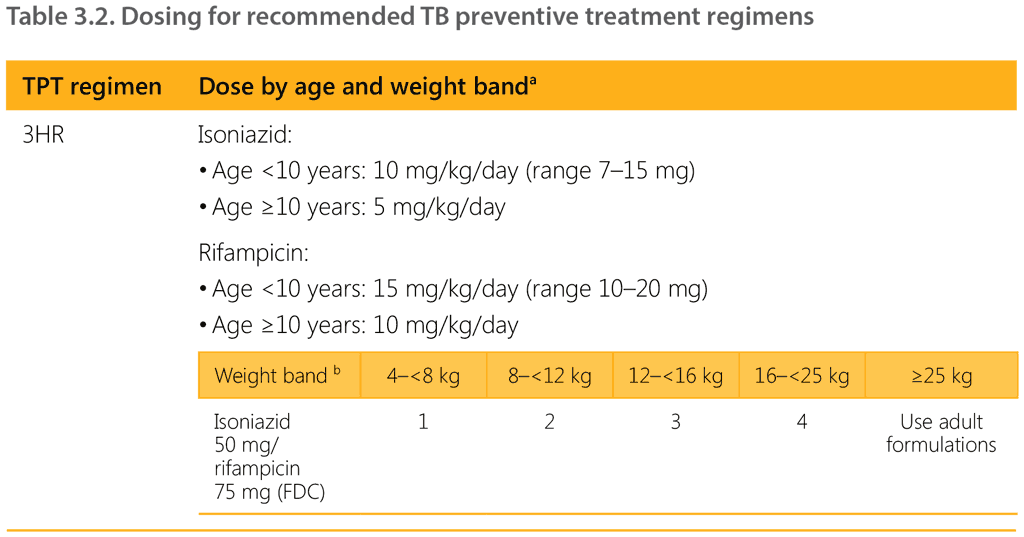
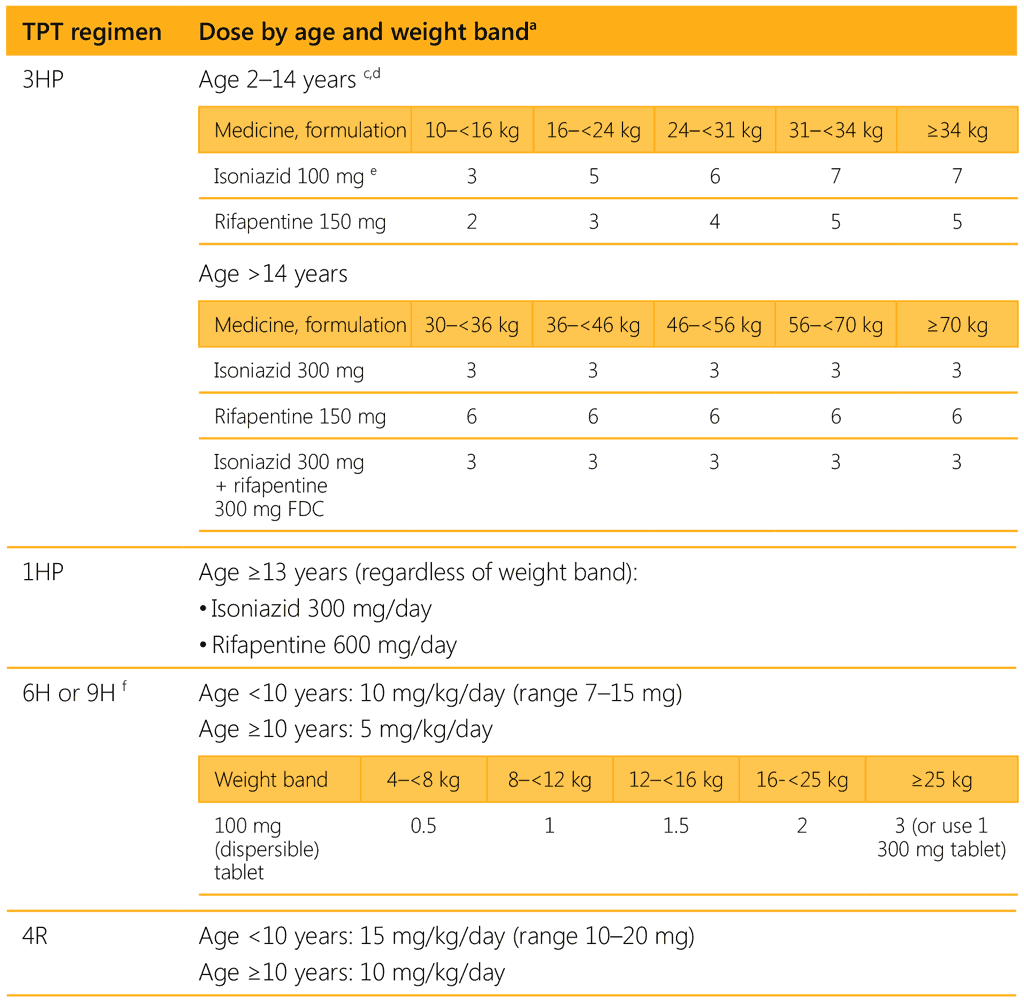
1HP: 1 month of daily isoniazid and rifapentine (28 doses); 3HP: 3 months of weekly isoniazid and rifapentine (12 doses); 3HR: 3 months of daily isoniazid and rifampicin; 4R: 4 months of daily rifampicin; 6H: 6 months of daily isoniazid; 9H: 9 months of daily isoniazid.
a Presentation of weight bands has been updated – for example, the 4–7 kg weight band is now written as 4–<8 kg. There is no change to the weight range represented in the weight band.
b For infants weighing less than 4 kg, consult a paediatric TB specialist.
c Dosage may differ among adults and children in overlapping weight bands.
d For children aged 2 years and over but weighing less than 10 kg, consult a paediatric TB specialist before using 3HP.
e A 300 mg formulation can be used to reduce the pill burden.
f A triple pill combination containing isoniazid 300 mg + pyridoxine 25 mg + sulfamethoxazole 800 mg + trimethoprim 160 mg (co-trimoxazole) (scored) is the preferred alternative regimen for people living with HIV being considered for isoniazid monotherapy (1 tablet daily for adults, 0.5 tablet daily for children aged over 5 years, 0.25 tablet daily for children aged under 5 years).
A side-effect of long-term treatment with high-dose isoniazid is peripheral neuropathy, which develops secondary to a deficiency of vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) during treatment. People at risk for peripheral neuropathy, such as those with malnutrition, HIV, renal failure or diabetes, or who are pregnant or breastfeeding, should receive vitamin B6 supplements when taking an isoniazid-containing regimen. Additionally, exclusively breastfed infants should receive vitamin B6 while taking isoniazid (15). In children living with HIV and malnourished children, daily pyridoxine supplementation may be added for the duration of TPT containing isoniazid (5–10 mg daily in children aged under 5 years; 25 mg daily in children aged over 5 years) (6).
 Feedback
Feedback