Book traversal links for 7.1.7.3. Adjustments to antiretroviral therapy regimens with TB treatment
In people with TB/HIV coinfection, the dose of DTG needs to be doubled by giving it twice instead of once a day because of drug–drug interactions with rifampicin. This extra dose of DTG is well tolerated, with equivalent efficacy in viral suppression and recovery of CD4 cell count compared with EFV (182, 183).
Table 7.2 summarizes changes needed to ART regimens for neonates, children and adolescents who are on ART when TB treatment is started, or who start ART while on TB treatment.
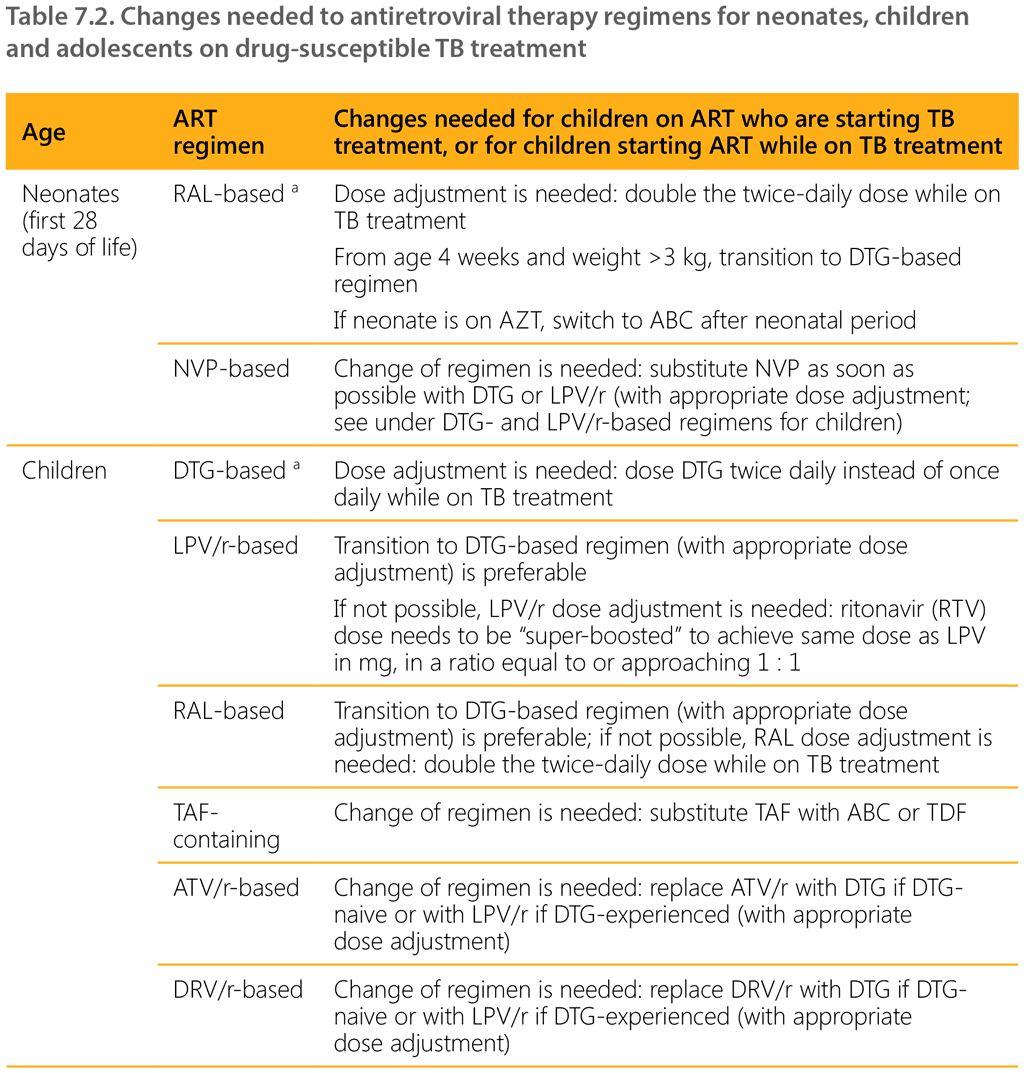
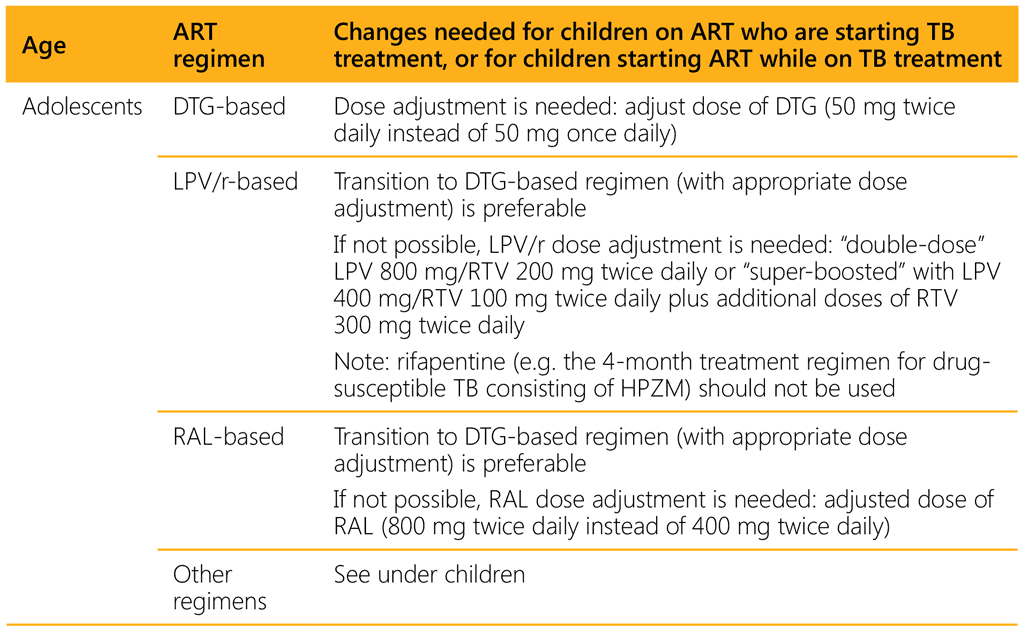
a Preferred ART regimen for initiation in neonates and children on TB treatment.
3TC: lamivudine; ABC: abacavir; ATV/r: atazanavir/ritonavir; AZT: zidovudine; DRV/r: darunavir/ritonavir; DTG: dolutegravir; EFV: efavirenz; FTC: emtricitabine; LPV/r: lopinavir/ritonavir; NVP: nevirapine; RAL: raltegravir; RTV: ritonavir; TAF: tenofovir alafenamide; TDF: tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.
For details on dosing of ART medicines with TB treatment in neonates, children and adolescents, see the interactive dosing table at https://paedsarvdosing.org. A useful tool for checking drug–drug interactions is at https://www.hiv-druginteractions.org/.
 Feedback
Feedback