Book traversal links for Annex 2 Comparative performance of algorithms for the general population and high-risk groups (not including people living with HIV)
The tables below contain modelled estimates of the performance and outcomes of the 10 screening algorithms described above, when applied to a population of 100,000 people being screened, across three different TB prevalence settings: 0.5%, 1% and 2%.
1 – Screening with cough
2 – Parallel screening with cough and CXR
3 – Sequential positive serial screening with cough and CXR
4 – Sequential negative serial screening with cough and CXR
5 – Screening with any TB symptom
6 – Parallel screening with any TB symptom and CXR
7 – Sequential positive serial screening with any TB symptom and CXR
8 – Sequential negative serial screening with any TB symptom and CXR
9 – Screening with CXR followed by mWRD
10 – Screening with mWRD followed by diagnostic exam (consisting of repeated mWRD, CXR, other clinical tests and procedures as indicated)
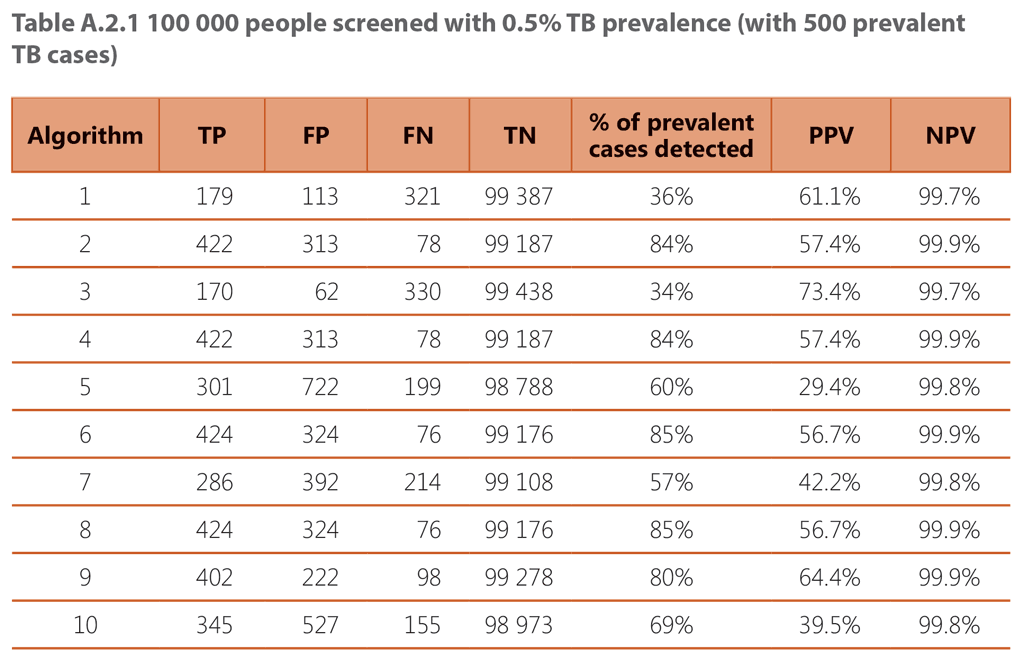
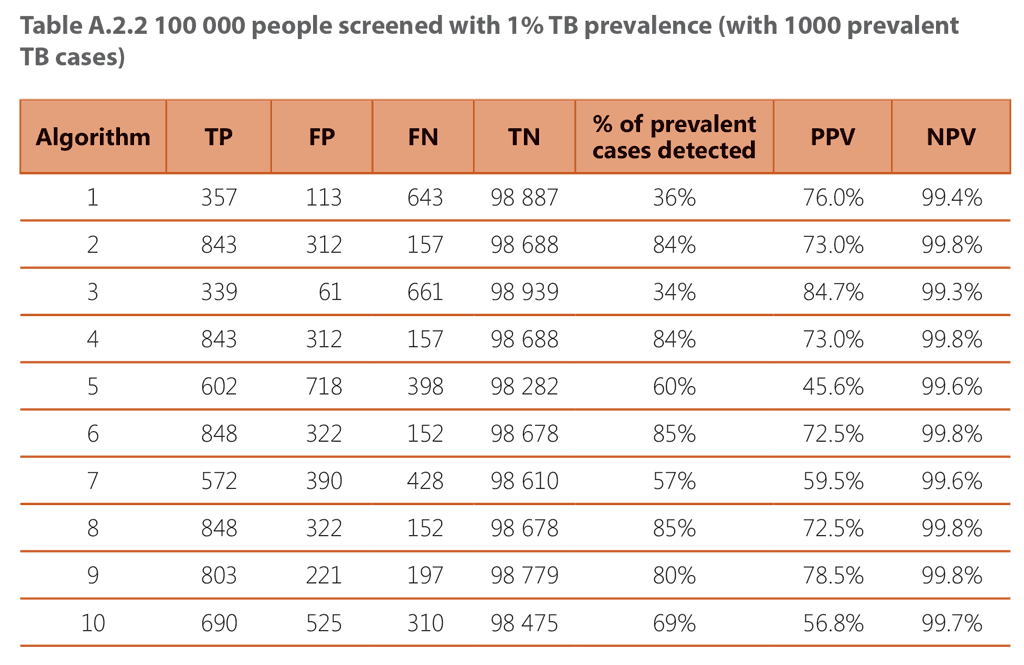
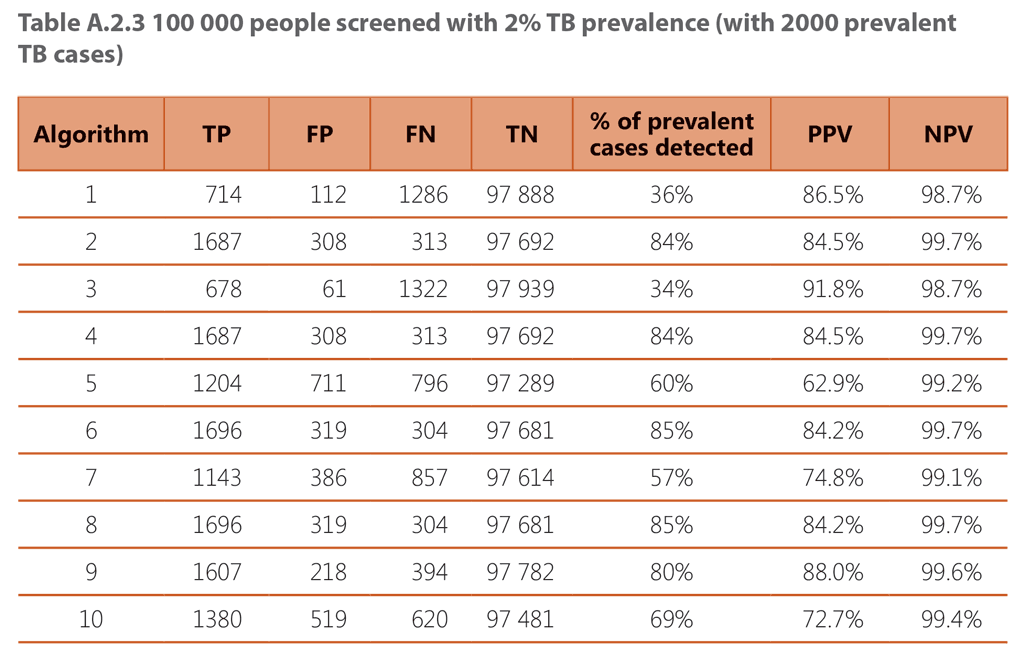
TP – True positive diagnosis
FP – False positive diagnosis
FN – False negative diagnosis
TN – True negative diagnosis
PPV – Positive predictive value
NPV – Negative predictive value
 Feedback
Feedback