Book traversal links for 5.2.4 WHO-recommended rapid molecular diagnostic tests
mWRDs are now also recommended for screening people living with HIV. (See 3.1.4 for a full description of their use in screening). A positive mWRD screen result in a person with HIV must be followed by further diagnostic evaluation to confirm or rule out TB.
Among medical inpatients in settings where the prevalence of TB is ≥ 10%, mWRDs are strongly recommended for screening for TB disease because of the severity of illness in this population. As rapid diagnosis and care are required, a positive mWRD result in this population can be considered an indication for treatment and need not be followed by a separate diagnostic evaluation, while ensuring proper monitoring of treatment response and evaluation for alternative diagnoses, particularly if the patient had TB in the previous 5 years.
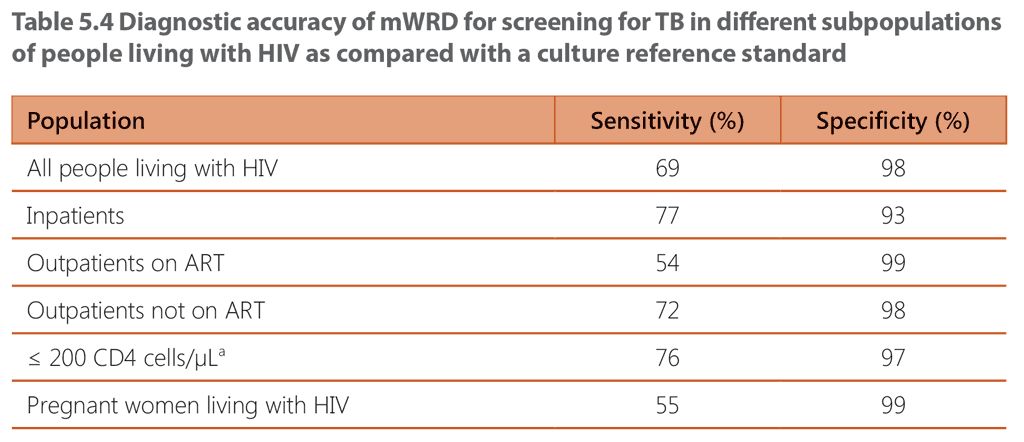
Table 5.4 shows the accuracy of mWRD screening in different sub-populations of adults and adolescents living with HIV. The overall sensitivity of mWRD in all people living with HIV is estimated to be 69% and the specificity 98%, while W4SS followed by a mWRD is estimated to have a sensitivity of 62% and a specificity of 99% (see Web Annex B of the guidelines). The accuracy of mWRD in most subpopulations is not significantly different from that of W4SS followed by mWRD.
For more detail, see Web Annex B of the screening guidelines.
ᵃ Indicator of advanced HIV disease
 Feedback
Feedback