Перекрёстные ссылки книги для Annex 2: Information sheets on the newly recommended products
Culture-based DST methods for certain anti-tuberculosis (anti-TB) medicines are reliable and reproducible, but these methods are time consuming, and require specific laboratory infrastructure, skilled staff and adherence to quality control. The manual in Web Annex C (WHO Technical manual for culture-based drug susceptibility testing of medicines used in the treatment of tuberculosis) describes the methods, media, sources of drug powders and critical concentrations for conducting drug susceptibility testing (DST) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC isolates). Only indirect phenotypic DST procedures for anti-TB medicines are described in this document; they include Löwenstein–Jensen (LJ), 7H10 agar,7H11 agar and 7H9 broth (BACTEC Mycobacterial Growth Indicator Tube [MGIT] instrument). The manual incorporates recent revisions to critical concentrations for rifampicin (1) as well as newly developed critical concentrations for pretonamid and cycloserine (Web Annex B).
Key topics in the manual are:
- biosafety;
- evidence basis for determining critical concentrations for DST;
- recommendations for DST for first-line anti-TB agents;
- recommendations for DST for second-line anti-TB agents;
- susceptibility testing for anti-TB agents using the proportion method on solid media (LJ medium, or Middlebrook 7H10 or 7H11 agar media):
- anti-TB agents and critical concentrations for testing;
- recommended drug powders and preparing solutions of anti-TB agents;
- preparing the mycobacterial suspension;
- diluting the suspension and inoculating the medium;
- interpreting and reporting results;
- quality control;
- susceptibility testing for anti-TB agents using liquid media (MGIT):
- anti-TB agents and critical concentrations for testing;
- recommended drug powders and preparing solutions of anti-TB agents;
- preparing the mycobacterial inoculum;
- diluting the suspension and inoculating the liquid medium;
- interpreting and reporting results; and
- quality control.
Recommended critical concentrations for testing anti-TB medicines are presented in Tables 2.2 and 2.3 in Section 2.6 of the main text. Table A2.1 lists available pure powders and their sources.
Table A2.1. Availability of pure powders from GDF and other manufacturers
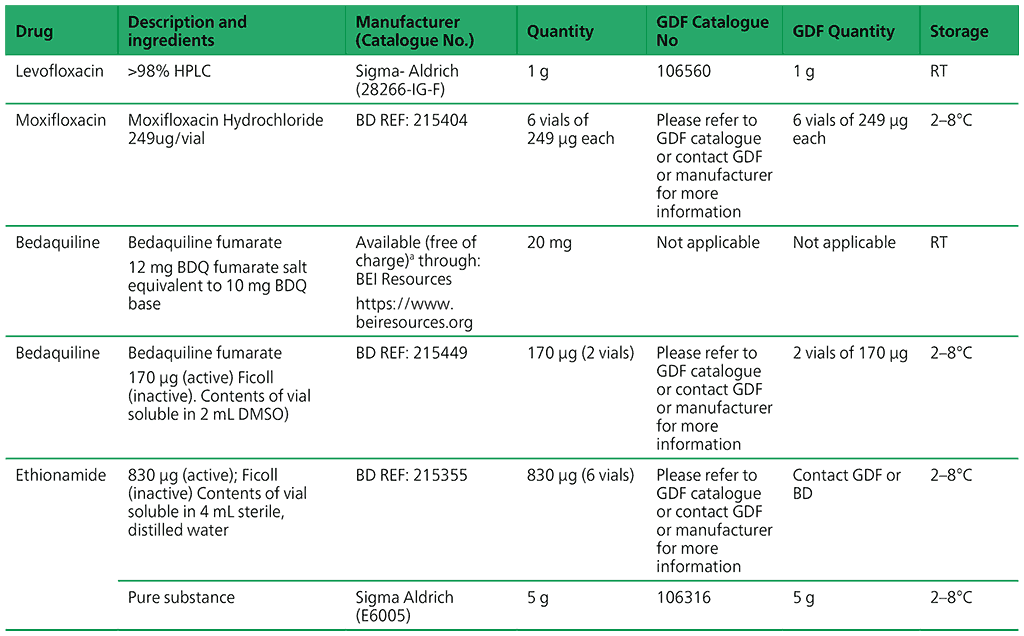
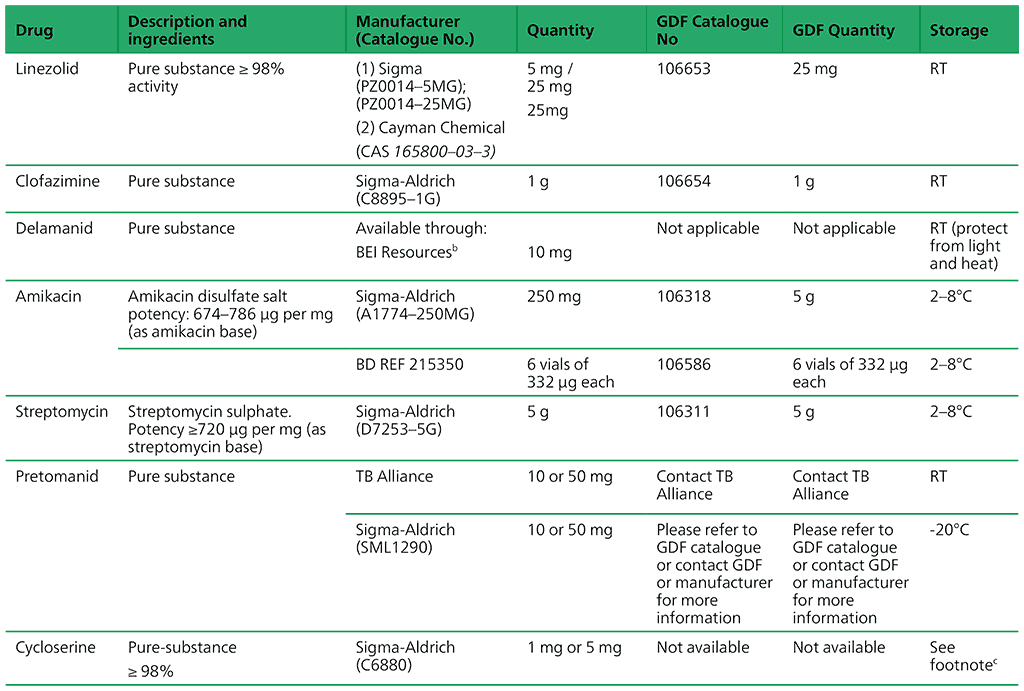
a Free of charge shipment when specifying carrier as JNJ
b Collection from the closest airport and customs clearance of the drug shipment is the responsibility of the receiving laboratory
c Given the known heat instability of DCS, DCS powder should be stored as instructed by the manufacturer and stocks solutions in sterile distilled/deionised water should be stored at –70° C ± 10° C for no longer than six months (i.e. lower temperatures should not be used and vials should never be re-frozen).
RT – room temperature
Reference for Annex 2
- Technical report on critical concentrations for drug susceptibility testing of isoniazid and the rifamycins (rifampicin, rifabutin and rifapentine). Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021 (https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240017283).
 Обратная связь
Обратная связь